What is the Production Process of Tube Mill Machine?
You are here: Home>Industry Information>What is the Production Process of Tube Mill Machine?
What is a Tube Mill Machine?
A tube mill machine is used to produce welded pipes, also known as longitudinal welded pipe machines. These machines are commonly used in steel pipe factories for producing various specifications of welded pipes. They are widely used in industries such as construction, automotive, and furniture manufacturing.

The working principle of a tube mill
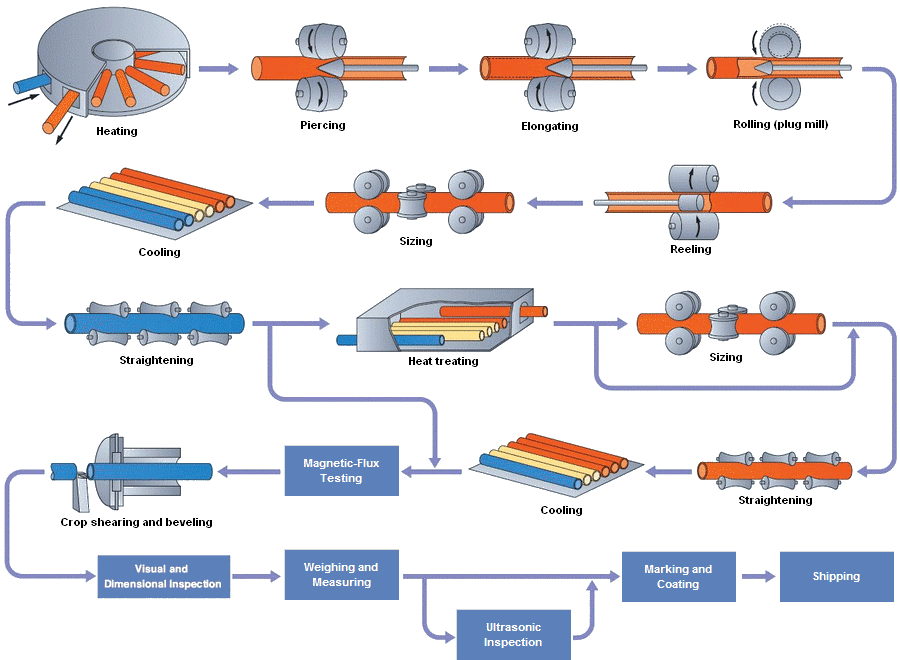
Uncoiling
- Process: The steel strip, usually in coil form, is fed into the tube mill line through an uncoiler.
- Purpose: To continuously supply the steel strip to the mill for further processing.
Leveling
- Process: The steel strip passes through a leveling machine to remove any curvature or irregularities.
- Purpose: Ensures a flat, uniform strip before forming.
Shearing and End Welding
- Process: The steel strip is sheared to the required width, and if necessary, ends are welded together to ensure continuous operation.
- Purpose: To create a seamless transition between coils and maintain a consistent production flow.
Forming
- Process: The leveled strip enters the forming section, where a series of forming rolls gradually shape it into a round tube.
- Purpose: To form the steel strip into a tubular shape, preparing it for welding.
Welding
- Process: The edges of the formed tube are heated and pressed together to create a longitudinal weld, usually through Electric Resistance Welding (ERW) or high-frequency welding.
- Purpose: To join the edges of the steel strip, forming a continuous steel pipe.
Sizing
- Process: The welded tube passes through a sizing section, where rolls further refine the tube to the desired dimensions and roundness.
- Purpose: Ensures that the tube meets precise diameter and thickness specifications.
Cooling
- Process: The welded and sized tube is cooled, typically using water, to set its shape and properties.
- Purpose: To solidify the tube’s structure and make it ready for further processing.
Cutting
- Process: The continuous tube is cut to the desired length using a flying saw or a rotary cutter.
- Purpose: To produce individual steel pipes of the required length.
End Facing and Beveling
- Process: The pipe ends are machined to remove burrs and achieve the required end shape, such as beveling for welding.
- Purpose: Prepares the pipe ends for further joining or other applications.
Inspection and Testing
- Process: The finished pipes undergo various inspections and tests, including visual inspection, hydrostatic testing, and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic testing.
- Purpose: To ensure the pipes meet quality standards and specifications.
Packaging and Dispatch
- Process: The pipes are bundled, tagged, and prepared for shipping.
- Purpose: To protect the pipes during transportation and provide relevant identification for delivery.
Key Components of a Tube Mill Machine
Uncoiler
Uncoilers the hot-rolled steel coil and feeds it into the leveling machine. There are two uncoiling methods: upper uncoiling and lower uncoiling.
Steel Strip Leveler
Levels the steel strip before forming.
Shear and End Welder
Ensures continuous production by trimming the irregular ends of the steel strips and welding them together.
Accumulator
Stores the pre-leveled steel strip and continuously feeds it to ensure uninterrupted production.
Forming Section
Shapes the running steel strip into the form of a pipe.
High-Frequency Welding Device
Commonly uses a solid-state high-frequency welder to weld the formed steel strip into a steel pipe.
Sizing Section
Ensures the accuracy of the pipe’s outer diameter and cross-sectional shape, improving the stress concentration and residual stress from forming and welding.
Flying Saw
Cuts the running steel pipe to the desired length with high precision.
Packaging Machine
Collects the finished steel pipes and packages them into fixed shapes.

Step-by-Step Production Process of Tube Mill Machine
1. Raw Material Preparation and Feeding Process
Inspect the appearance and dimensions of the steel strip coil. Once confirmed, use the feeding cart to place the steel strip coil onto the uncoiler.
2. Material Feeding
The prepared steel strip is fed into the machine through the uncoiler. The strip passes through the shear and end welder, welding the strip ends to create a continuous feed, minimizing downtime.
3. Accumulation
The accumulator stores the steel strip, ensuring a continuous and uninterrupted supply to the forming section.
4. Pipe Forming
In the forming section, the steel strip is gradually bent into a round pipe through a series of rollers.
5. Welding
The edges of the formed pipe are welded together using a high-frequency solid-state welder.
6. Sizing
The welded pipe passes through the sizing section, where its diameter and roundness are precisely adjusted. The rollers on the stands adjust the pipe’s dimensions to meet the required specifications.
7. Cutting
After sizing, the pipe is cut to the desired length by the flying saw in the cutting section.
8. Pipe Stacking
The pipes are collected and stacked into the desired shapes for customers, undergoing quality and defect inspections. Pipes that do not meet the standards are removed for reprocessing or scrapping.
Conclusion
The production process of a tube mill machine is a complex and precise operation that requires careful attention to detail at every stage. From raw material preparation to final quality control checks, each step is essential for producing high-quality tubes and pipes. Understanding the tube mill machine process can help manufacturers improve efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure the production of superior products.
Products
- Round Pipe Change to Square Tube Mill
- Small Diameter Thick Wall Tube Mill
- Roller Quick Change System Tube Mill
- Large Diameter Direct Forming Square Tube Mill
- TD 38 Tube Mill(12-38mm)
- TD 50 Tube Mill(25-63mm)
- TD 76 Tube Mill(32-89mm)
- TD 114 Tube Mill(42-119mm)
- TD 127 Tube Mill(42-127mm)
- TD 219 Tube MIll(89-219mm)
- TD 273 Tube MIll(114-273mm)
- TD 325 Tube MIll(127-325mm)
- Slitting Line
- Cut to Length Line
- Cold Roll Forming Machine
